LOINC - Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes
Standards make health data more portable and understandable to different computer systems.
The universal standard for identifying health measurements, observations, and documents.
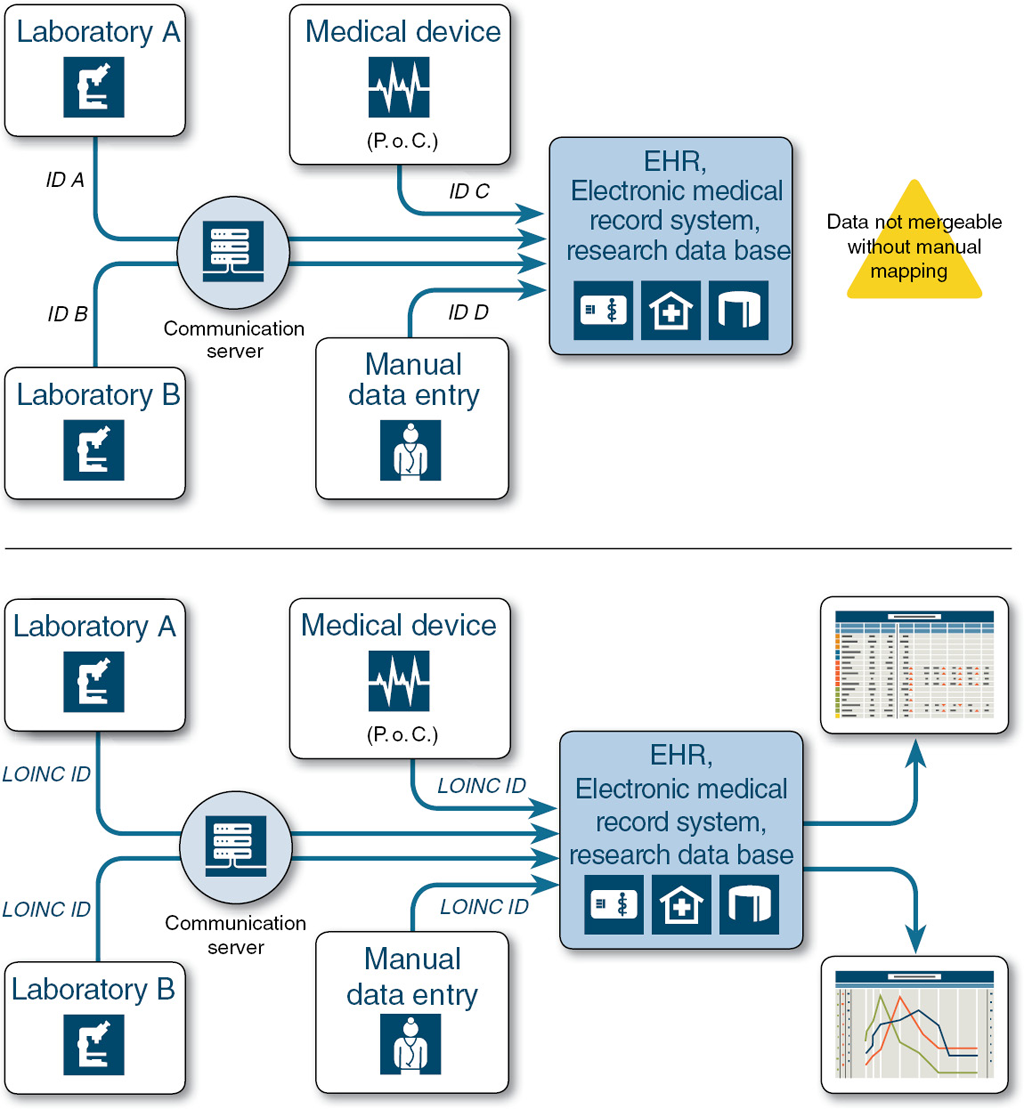
LOINC facilitates the exchange and pooling of results for clinical care, outcomes management, and research. LOINC codes are intended to identify the test result or clinical observation. Other fields in the message can transmit the identity of the source laboratory and special details about the sample.
What LOINC is
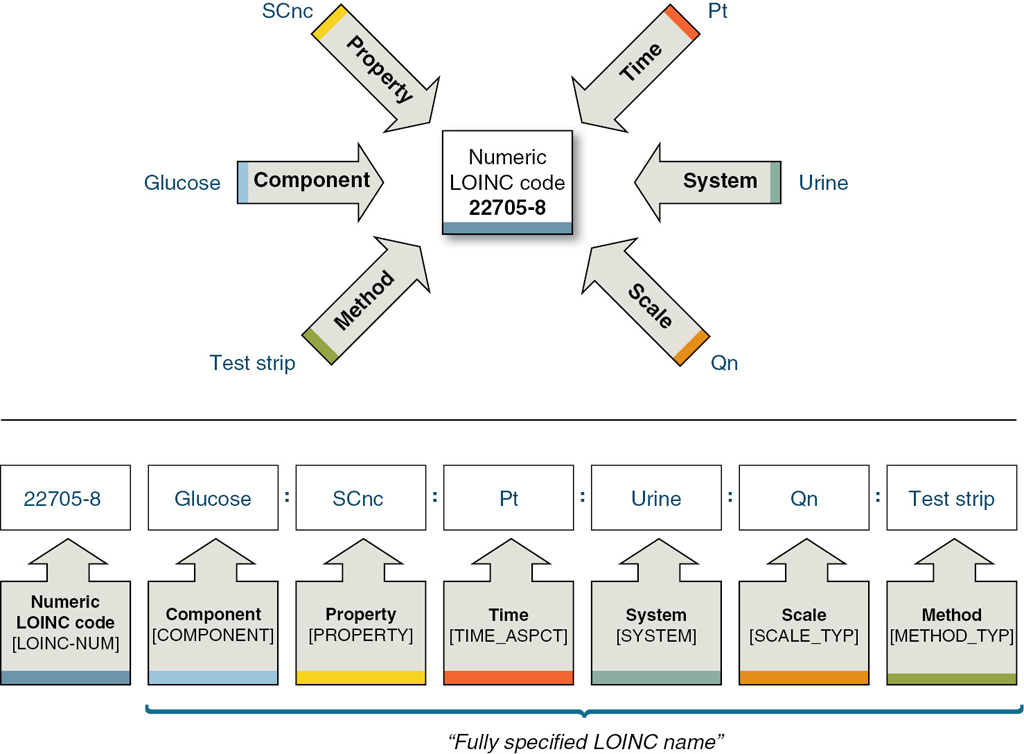
LOINC is published biannually by the Regenstrief Institute as a database of unique codes associated with human-readable terms. Each code corresponds to a distinct lab test (currently 55,844 out of 91,388 codes) or another clinical observation explicitly defined by five mandatory main dimensions plus an optional method part. Therein, LOINC's referenced properties are restricted to those required for a correct test result interpretation so that each combination represents the minimal set of values needed to distinguish this test from all others. For most axes, some further information can be included in specific subcomponents if needed for a full definition.
LOINC is a common language (set of identifiers, names, and codes) for identifying health measurements, observations, and documents. If you think of an observation as a "question" and the observation result value as an "answer." LOINC codes represent the "question" for a test or measurement
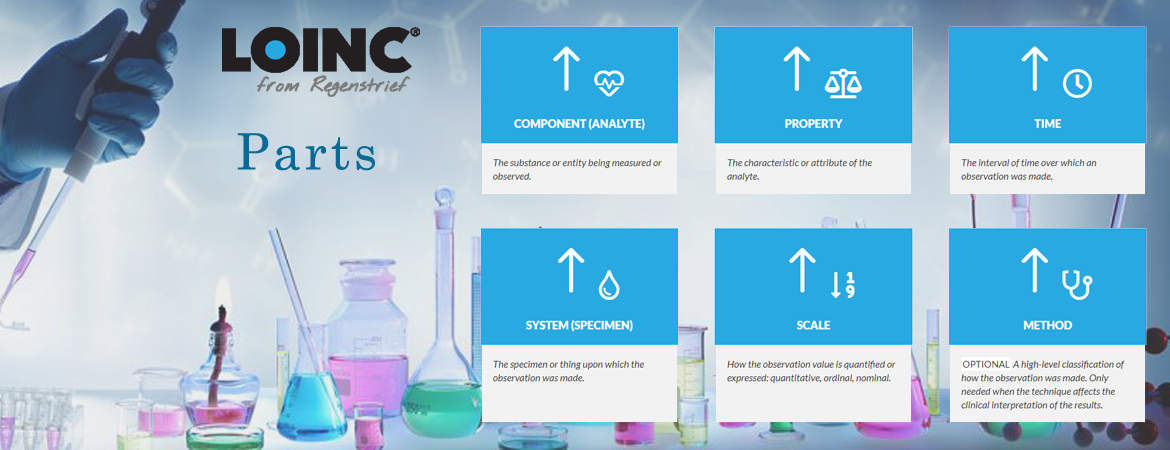
Component describes the kind of substance or analyte measured stating the test's most basic information with an immense variety of possible values (currently 24,707 part codes) and complexity of contents (up to three subcomponents).
Property denotes in which characteristic or type of property the component was measured, e.g. as number, as substance concentration or the qualitative presence. Obviously, this value is highly correlated with the test result's unit which is not specified in the LOINC term [5]. With 135 different options, the property axis is known to cause misunderstandings and therefore issues while mapping to LOINC [6].
Time Identifies whether the measurement is made at a point in time or a time interval. Interval measurements often apply to urine and stool (e.g., collection over 24 hours and calculation of a concentration, total amount, or clearance). They also apply to clinical measurements, such as urine outputs where we have shift totals and 24-hour totals. E.g. 24H for a urine sodium concentration.
System defines the specimen or material sample used for testing as the second most distinct characteristic. Further refinement is typically needed by other properties (e.g. 32 LOINC codes for “creatinine” in “urine”) or a subcomponent.
Scale broadly differentiates between quantitative, ordinal and nominal measurements, forming an interrelation to the Property part. Answer options for qualitative tests shall be coded with SNOMED CT; for quantitative results exemplary value ranges and units are partially mentioned but not explicitly defined.
Method information is only included if the measurement technique is clinically significant by affecting the test's result or reference range. So, most terms (63.32%) lack this dimension.
About LOINC
LOINC is a set of identifiers, names and codes for identifying health measurements, observations and documents. It is owned, maintained and distributed by Regenstrief Institute, Inc USA. A universal code system will enable facilities and departments across the world to receive and send results from their areas for comparison and consultation and may contribute toward a larger public health initiative of improving clinical outcomes and quality of care. A formal, distinct, and unique 6-part name is given to each term for test or observation identity. The database currently has 84868 terms that can be accessed and understood universally. LOINC has two main parts: laboratory LOINC and clinical LOINC.